Alkaline ionized water is slightly alkali electrolyzed water with a pH of 9 to 10 created on the cathode side by direct-current electrolysis of drinking water including calcium ions (when necessary, with the addition of calcium lactate, etc. as an electrolysis promoter) using an alkaline ionized water apparatus. (On the other hand, slightly acidic electrolyzed water generated on the anode side with a pH of 4 to 6 is termed “acidic ion water”.)
Further, the electrolysis promoter to be added is limited to calcium compounds approved as food additives.
As shown in the figure below, an alkaline ionized water apparatus generally has an electrolysis tank with the cathodes and anodes separated by a barrier membrane such as an ion exchange membrane, and the barrier membrane has the function of allowing the passage of ions in the water but preventing the passage of the water itself.
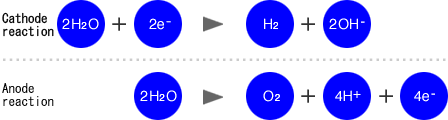
Raw water containing calcium ions is put into the electrolysis tank. When a direct voltage is applied, direct current flows and the positive ions (M+) such as calcium ions, magnesium ions, potassium ions, sodium ions, etc. are attracted to the cathode, and the negative ions (X-) such as chloride ions, carbonate ions, sulfate ions, nitrate ions, etc. are attracted to the anode.
in other words, hydroxide ions (OH-), positive ions, and hydrogen (H2) become more numerous on the cathode side, and alkaline ionized water with high pH is generated, while on the anode side, hydrogen ions (H+), negative ions, dissolved oxygen (O2), etc. become more numerous, and (slightly) acidic water with low pH is generated.
Further, the conditions of the alkaline ionized water and slightly acidic water are as shown below.
| pH | Oxidization reduction potential | Positive ions | Negative ions | Generated substances | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline ionized water | Around 9 to 10 | Decreased (Reduction potential) | Increased | Decreased | Hydrogen; Calcium hydroxide |
| Acidic water | Around 4 to 6 | Increased (Oxidation potential) | Decreased | Increased | Oxygen; Chlorine |
The drinkable range for alkaline ionized water is defined as being pH9 to 10, and strongly alkaline electrolytic water with pH exceeding pH10 cannot be used directly for drinking.
In addition, the calcium concentration of alkaline ionized water is increased by 30 to 50% compared to tap water.
Further, the name “alkaline ionized water” is the popular name, and “alkaline electrolytic water for drinking” is the name generally used. (From the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Notification No. 112)
Although names such as “alkaline water”, “ion water”, or “electrolyzed reduced water”, etc. are also used, if the generation apparatus for functional water for drinking purposes is a type labeled with a “medical device approval (certification) number”, it has been approved and certified as a medical device after undergoing unified evaluation, and so the same electrolytic water is generated.
Currently, no electrolytic water other than alkaline ionized water has been approved for drinking. (However, care must be exercised since even if a product has been certified as medical apparatus, it cannot produce the same alkaline ionized water if it is not used properly with the correct pH value, used raw water, etc. according to the instruction manual.)